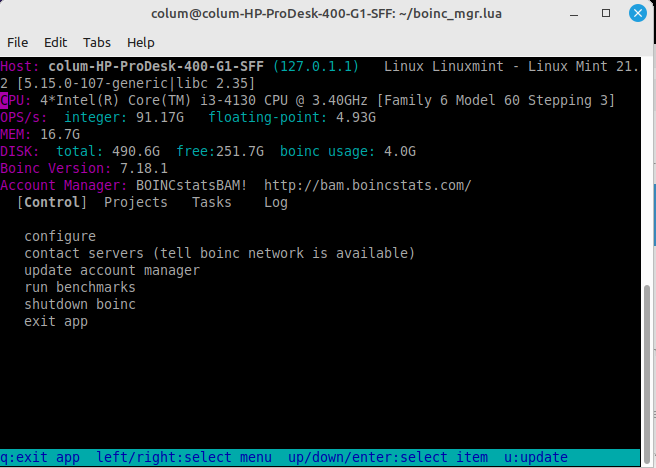

boinc_mgr.lua is a menu-driven text-mode lua program for managing the boinc client app. It requires libUseful (at least version 4.0) and libUseful-lua (at least version 2.18) to be installed. boinc_mgr.lua can start and stop the boinc client app on local host, can join, attach, and detach from projects, and can start/stop tasks. It can also attach to boinc over tcp, and over tcp-over-ssh.
Menus are navigated using either the arrow keys, or ctrl-WASD keys (the latter requires a libUseful version > 4.52).
boinc_mgr.lua [host] [-key gui-key] [-user username] [-email email-address] [-pass password] [-save]
host - host to connect to. e.g. "tcp:192.168.2.1" or "ssh:myserver"
-key [gui-key] This supplies the gui-key for a boinc process. This is needed for most control operations.
This key is normally found in the file "gui_rpc_auth.cfg" in whatever directory the boinc
process is running in.
-save save the gui-key.
-acct_mgr [url] Set account manager. This requires -user and -pass for the account manager login.
'-acct_mgr none' disconnects from any currently configured account manager.
-user [name] Username. Needed for creating/joining project accounts and other management tasks.
-email [email] email address. Needed for creating/joining project accounts
-pass [passwd] password. Needed for creating/joining project accounts and other management tasks.
Assuming you’ve used the same user, email and pass for all projects, the user, email, and pass can be set within the program itself, so that they don’t need to be passed on the command-line every time. The gui-key can be saved on a per-host basis by using the “-save” option. This will save the key for the current host in “~/.boinc/keys.txt”, allowing multiple hosts to be accessed without needing to pass in the key.
If you’re using an account manager you can set it by passing the url with the -acct_mgr option. This also requires the ‘-user’ and ‘-pass’ options to supply the username and password for the account manager. Once the account manager is set these options do not need to be passed in again, and the username and password are never stored on disk.
You can set things back to having no account manager with ‘-acct_mgr none’.
Hosts that are accessed via SSH must be configured in the ~/.ssh/config file with an ssh key.
If run without any arguments the program will try to connect to a boinc process at “tcp:localhost”. If it can’t connect it will offer to start a new boinc process in “~/.boinc” and store the key for it.
Boinc manager can connect to boinc processes running on remote machines, either over tcp, or over ssh. The default port for boinc is 31416, so this
boinc_mgr.lua tcp:192.168.2.10 -key boinc-key.192.168.2.10
Would connect to a remote boinc at 192.168.2.10.
If a nonstandard port is in use, (e.g. 3333) the command-line becomes:
boinc_mgr.lua tcp:192.168.2.10:3333 -key boinc-key.192.168.2.10
Obviously for tcp connections the boinc service must be connectable (firewall open for the appropriate port).
Alternatively boinc can use ssh tunneling:
boinc_mgr.lua ssh:myboinchost -key boinc-key.myboinchost
For this to work, ‘myboinchost’ must be set up as a preconfigured host in ~/.ssh/config
ssh connections expect to tunnel via ssh to the default boinmc port on the remote machine.
Note that in all these cases you need to have a copy of the boinc key for the boinc process on the machine that is running boinc_mgr, and supply that via the ‘-key’ command-line argument.
 https://github.com/ColumPaget/boinc_mgr.lua
https://github.com/ColumPaget/boinc_mgr.lua